For the best diabetic diet, limit carbohydrates with added sugars or refined grains and focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, and low-fat dairy. These choices help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Additionally, plant-based diets rich in fiber, antioxidants, and magnesium have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and overall glycemic control. Superstar foods for people with diabetes include beans, dark green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, berries, tomatoes, nuts, and whole grains. Incorporating these nutrient-dense foods into your diet can better manage your diabetes and improve your overall health.
Remember to consult a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to create a personalized plan that suits your needs and preferences.

Credit: www.healthline.com
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is when the body can’t produce or properly use insulin. There are different types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Managing diabetes is crucial to preventing complications and maintaining overall health. It’s best to avoid foods with added sugars and refined grains. Instead, focus on carbohydrates from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, and low-fat dairy.
Additionally, including foods rich in nutrients like beans, dark green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, and nuts can be beneficial. A healthy eating plan for diabetes includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while incorporating protein foods and limiting processed carbs. A balanced diet with these food groups can help manage diabetes effectively.
Dietary Recommendations For Diabetics
Limit carbohydrates with added sugars by choosing whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Importance of fiber and antioxidants in your diabetes diet.
Beans, dark green leafy vegetables, citrus fruit, berries, tomatoes, nuts, and whole grains are superstar foods for diabetes.
Popular Diets For Diabetics
The DASH Diet reduces sodium intake and promotes a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables. The Mediterranean Diet emphasizes healthy fats such as olive oil. It incorporates whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of fresh produce. The Flexitarian Diet encourages plant-based eating with the flexibility to include small amounts of meat. The Ornish Diet is centered around whole, plant-based foods, and limits sugar and processed foods. The Mind Diet combines elements of the Mediterranean and DASH diets to support brain health.
Building A Healthy Eating Plan
When managing diabetes, it’s essential to build a healthy eating plan that includes a variety of fruits and vegetables. These should comprise a large part of a diabetic’s diet as they are high in essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Regarding starchy foods and whole grains, opt for options high in fiber and low in added sugars. Protein foods play a crucial role in a diabetic’s diet as well, and lean sources such as poultry, fish, and tofu are excellent choices. Additionally, incorporating dairy and low-fat and sugar alternatives can provide essential nutrients. Choose options high in unsaturated fats, such as olive oil and avocado, when using oils and spreads. By creating a balanced eating plan that includes these food groups, individuals with diabetes can better manage their condition and improve their overall health.
Meal Planning For Diabetes
| Subheading | Key Points |
|---|---|
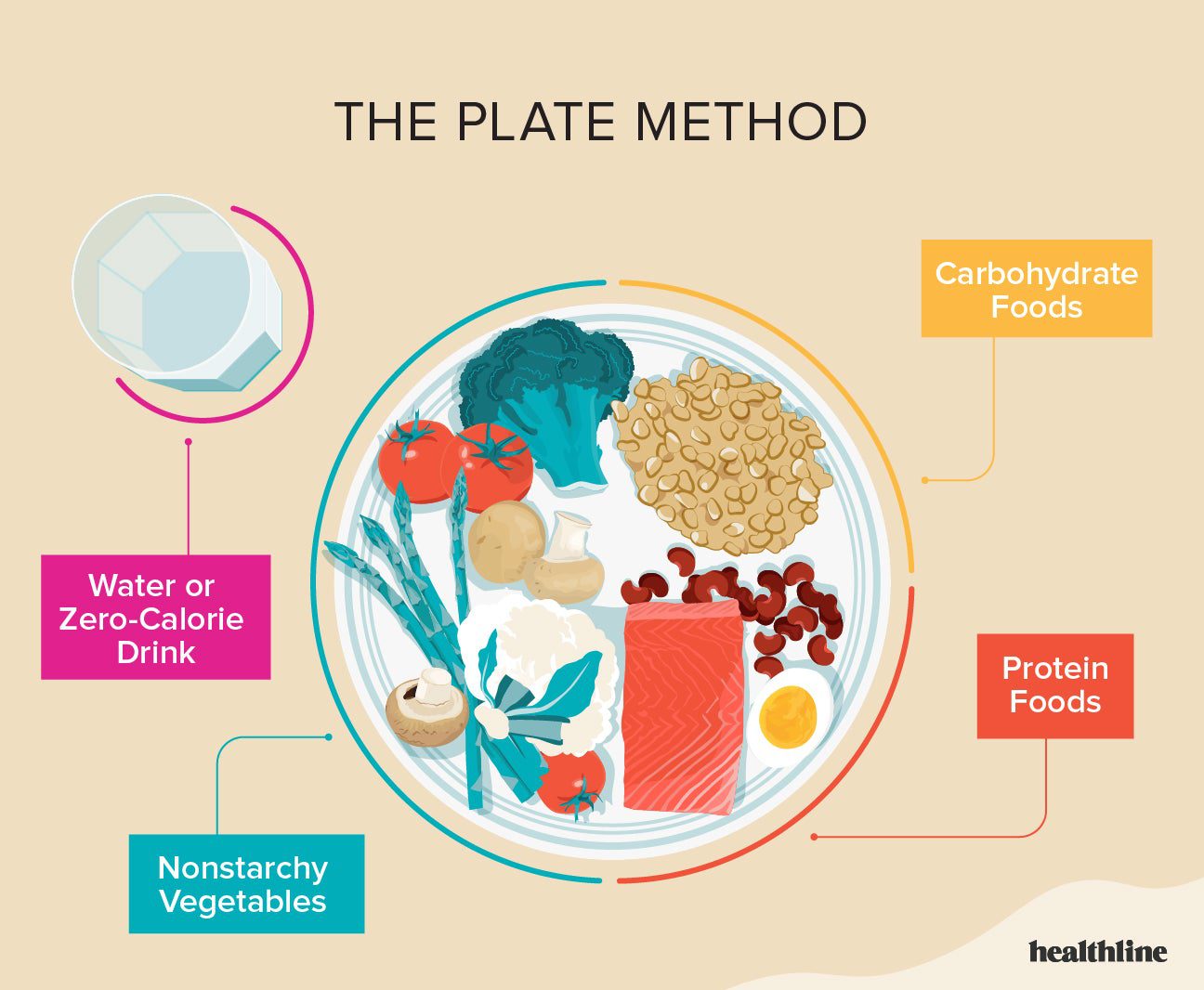
| Quarter plate method | Eat carbohydrates from fruit, vegetables, whole grains, beans, and low-fat or nonfat milk. Avoid carbohydrates with added sugars or refined grains, such as white bread and white rice. |
| Balancing carbohydrates | Limit intake of highly processed carbs like white bread and foods labeled ‘diabetic’. Include whole and minimally processed plant foods in your diet to reduce insulin resistance and improve glycemic control. |
| Healthful food choices | Include beans, dark green leafy vegetables, citrus fruit, berries, tomatoes, nuts, and whole grains in your diet. These foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber that promote insulin sensitivity. |
| Eating frequency | Create a healthy-eating plan rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Consume non starchy vegetables and moderate portion sizes to maintain a balanced diet for diabetes management. |
Note: The top five diets for people with diabetes are DASH, Mediterranean, Flexitarian, Ornish, and the Mind Diet. These diets emphasize the consumption of nutrient-rich fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.

Credit: www.baptisthealth.com

Credit: www.healthline.com
Dina is diabetic. Which diet would be best for her?
Managing diabetes involves making informed choices about one’s diet. For individuals like Dina, who has diabetes, selecting the proper diet is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and overall health. One of the most recommended diets for diabetic patients is the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes whole foods, healthy fats, and a balance of nutrients.
The Mediterranean diet includes a variety of fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, all of which are integral for blood sugar management. These foods have a low glycemic index, meaning they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. Additionally, the diet incorporates healthy fats from sources like olive oil, nuts, and fish, which can help improve cardiovascular health—essential for those managing diabetes, as they are at higher risk for heart disease.
Lean proteins from poultry, fish, and plant-based sources are also staples in this diet. These proteins are essential for repairing and building tissues without excessively raising blood sugar levels. Moreover, the Mediterranean diet is low in processed foods and sugars, which is detrimental to blood sugar control.
For Dina, adopting a Mediterranean diet could not only help stabilize her blood sugar but also contribute to a healthier lifestyle and better weight management. However, individuals with diabetes must consult a healthcare provider or dietitian to tailor dietary choices to their health needs. Ensures that the diet helps manage the disease and complements other aspects of the treatment plan.
By integrating these dietary changes, Dina can enjoy a diverse palette of foods that taste good and bolster her health against diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions On Which Diet Is Best For Diabetics?
What Is The Best Diet For A Diabetic?
The best diet for diabetics limits refined grains and added sugars. Instead, focus on carbohydrates from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, and low-fat or nonfat milk. Avoid foods labeled “diabetic” and minimize red and processed meat consumption.
Incorporate plant-based foods that are rich in fiber, antioxidants, and magnesium. Superstar foods for diabetes include beans, dark green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, berries, tomatoes, nuts, and whole grains. A healthy and balanced diet should include fruits, vegetables, starchy foods, protein foods, dairy alternatives, and healthy fats.
Overall, emphasize whole foods and maintain portion control.
What Food Should Diabetics Avoid?
People with diabetes should avoid foods high in added sugars and refined grains, such as white bread and white rice. They should also steer clear of foods labeled “diabetic” and reduce their intake of red and processed meat and highly processed carbohydrates.
For a healthier diet, opt for carbohydrates from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, and low-fat or nonfat milk.
What Is The Best Diet To Reverse Diabetes?
To reverse diabetes:
- Follow a plant-based diet rich in whole foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, and nuts.
- Avoid refined carbs and processed meats.
- Incorporate foods like beans, green leafy veggies, citrus fruits, berries, and whole grains into your diet.
What Are The 10 Best Foods For A Diabetic?
The ten best foods for people with diabetes are beans, dark leafy greens, citrus fruits, berries, tomatoes, nuts, whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins.
Conclusion
When managing diabetes, it is vital to make dietary choices to limit processed carbohydrates and focus on whole, minimally processed foods. Opting for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can improve glycemic control and reduce the risk of associated health issues.
Implementing these dietary changes can significantly impact a diabetic individual’s overall well-being.